“What are the common challenges companies face throughout the audit process?” It’s a question often asked by proactive leaders who want to avoid the missteps and oversights made by other organizations.
Many executives and corporate compliance leaders say there are simply not enough hours in the day to get everything done, or even to just move things forward in a timely manner. It’s also common for some employees to feel like their organization’s compliance strategy is reactionary, driven by customer requests rather than established as a strategic initiative from the top down – and they’re not wrong.
In this blog, we discuss the most prevalent audit challenges hindering organizations today and how the commitment to pursuing a quality audit can alleviate many of these common issues to pave the way for a more streamlined, efficient audit process.
Challenge: Limited staff resources and budget constraints
One of the most common challenges organizations face during the audit process is a shortage of sufficient staff resources and budget allocated to compliance. In fact, only 20% of companies have a dedicated compliance department – most put IT in charge of compliance.
That means IT professionals must manage compliance programs on top of their other responsibilities. Two-thirds of organizations spend at least 3 months each year preparing for each audit or assessment, which means teams in charge of compliance are spending a significant amount of time and money to prepare for and manage the process.
Because of this, it’s not surprising that many organizations find themselves strapped for resources and budget when it’s time to complete an audit. Some organizations may think the solution is to find the cheapest, quickest audit available so they can check the box and move on, but we believe that choosing the right partner will allow you to have an efficient process without sacrificing quality.
Solution: Choose an expert audit partner
Organizations faced with limited staffing and budget can alleviate these challenges by working with a seasoned auditor who acts as a trusted partner throughout the entire compliance journey. A-LIGN has decades of experience and technology to streamline the audit process and help your business work as efficiently as possible. By working with an expert audit firm, your team can free up valuable time and resources while ensuring your business is audit ready.
Challenge: Complexity in conducting multiple audits
Many businesses are tasked with adhering to numerous frameworks, resulting in the necessity to conduct more than one audit and/or assessment each year. A recent survey found that 92% of organizations conduct more than one audit each year. Given the depth of these unique frameworks, preparation for audits can be a time-consuming endeavor, and can even result in duplicated efforts across multiple audits. Organizations that have siloed teams or departments might also inadvertently gather the same evidence repeatedly to be used at various points in time.
Due to these complexities, many organizations find it difficult to allocate the correct resources to navigate different frameworks and complete all the required assessments in a timely, accurate manner.
Solution: Consolidate efforts across audits
Collaborating with an audit firm with expertise in a variety of frameworks can help streamline and consolidate your team’s audit efforts. With a breadth and depth of services, your audit team at A-LIGN will have the expertise to identify any overlaps to consolidate all your audits into one strategic audit plan. This ensures a consistent, standardized approach that provides a more comprehensive view of an organizations’ compliance posture. Plus, when leveraging A-LIGN’s audit management technology, users can easily link one piece of evidence to multiple audit requests, further streamlining efforts across frameworks.
By consolidating an audit into a single annual event, organizations can expect reduced employee workload and the ability to seamlessly and efficiently complete multiple audits. The efficiencies gained in audit consolidation also reduce the amount of time required to complete each audit.
Challenge: Tedious and manual evidence collection
The manual, repetitive tasks associated with evidence collection can plague the efficiency and quality of the audit process. With a scattered, de-centralized audit program spanning multiple vendors, different teams in an organization may spend dozens of hours searching for the same pieces of evidence. In an environment where teams have to do more with less, every hour counts. Manual evidence collection can result in a significant amount of time and resources that could be better allocated elsewhere.
Solution: Leverage GRC platforms
Organizations can save time and resources and streamline evidence collection when they work with an experienced auditor and leverage leading government, risk management, and compliance (GRC) technology.
With A-LIGN’s strategic partnerships with top GRC providers like Vanta, Drata, and AuditBoard, businesses can use integrations to ease the burden of evidence collection and foster an efficient audit process with the help of cutting-edge automation.
Comprehensive GRC software can also help with:
- Monitoring your security program in real time
- Gaining visibility into risks across your business
- Demonstrating compliance to customers via trust centers and questionnaire automation
Common challenges of the audit process: Key takeaways
In the face of challenges such as tedious evidence collection, staffing and budget constraints, and the complexity of managing multiple audits, many organizations find themselves adopting a reactive approach, often resulting in inefficiencies and disorganization during the audit process.
To address these issues, organizations should take a proactive approach to managing audits as a key business function. Working with an experienced audit partner, consolidating audit efforts, and leveraging leading GRC technology can create a more efficient audit process and allow teams to feel confident in their compliance strategy.
If you’re looking for a single provider approach for an efficient, high-quality audit experience, A-LIGN is here to help. Our experts will guide you through your assessment across the scope of each major framework while helping you get the most out of the audit process.
Ready to get started? Contact us today.
The Trusted Exchange Framework and Common Agreement (TEFCA) is a groundbreaking initiative within the healthcare sector, promoting integrated and secure health information exchange. This framework not only supports interoperability among Qualified Health Information Networks™ (QHINs), but also simplifies the sharing of patient data. Organizations under TEFCA must achieve HITRUST certification to uphold strict data protection standards. The partnership between TEFCA and HITRUST lays a robust foundation for health information exchange, enhancing patient privacy and security.
What is TEFCA?
TEFCA establishes a shared framework of principles, terms, and conditions to facilitate the creation of a standardized agreement. This agreement aims to facilitate the seamless exchange of electronic health information across diverse health information networks on a national scale.
Launched in December 2023, TEFCA’s primary goal is to advance the seamless flow of health information nationwide. The agreement is intended to ensure that healthcare providers, payers, and patients have secure, efficient access to health data, leading to better patient outcomes.
The Sequoia Project, a non-profit advocate for nationwide health information exchange, has been pivotal in developing TEFCA, serving as the Recognized Coordinating Entity (RCE). In this role, it’s responsible for crafting the Common Agreement and the QHIN Technical Framework, setting technical and governance requirements for Qualified Health Information Networks (QHINs) to ensure secure data exchange.
Collaborating with the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC), and stakeholders, The Sequoia Project ensures TEFCA’s visions translate into practice, enhancing healthcare delivery efficiency in the US.
What are the goals of TEFCA?
TEFCA plays a vital role in driving the US healthcare system towards efficiency and comprehensive care. The agreement aims to:
- Increase data access: Enable more secure and appropriate sharing of electronic health information to support existing user needs.
- Ensure core data availability: Guarantee a set of core data is shared across networks for treatment, individual access, public health, benefits determination, and certain payment and healthcare operations as defined by HIPAA.
- Reduce costs and improve efficiency: Minimize the need for multiple Health Information Network (HIN) memberships and legal agreements.
- Standardize privacy and security requirements: Offer a common framework for privacy and security, including standards for identity proofing and authentication, to protect patient data.
Who can participate in TEFCA?
TEFCA’s data exchange network is open to a wide range of healthcare organizations that successfully complete the comprehensive onboarding process, ultimately being designated as QHINs. These organizations include hospitals, health systems, payers, HIES, and other entities engaged in the management, exchange, or analysis of healthcare data.
To achieve QHIN status, an organization must demonstrate rigorous adherence to TEFCA’s technical, privacy, and security requirements. Additionally, these entities are mandated to maintain a commitment to interoperability, ensuring that health information can be securely shared across the care continuum to improve patient outcomes and streamline healthcare delivery.
As of February 2024, seven organizations have completed the rigorous approval process and have been designated as QHINs able to exchange health data across the nation via TEFCA:
- CommonWell Health Alliance
- eHealth Exchange
- Epic Nexus
- Health Gorilla
- Know2
- KONZA
- MedAllies
HITRUST Certification Requirements for QHINs in TEFCA
HITRUST Certification is a gold standard for compliance in the healthcare industry, providing a comprehensive security framework that aligns with existing standards and regulations, like HIPAA. As an internationally recognized benchmark for safeguarding sensitive information, HITRUST Certification demonstrates an organization’s commitment to protecting healthcare data.
As a part of TEFCA, QHINs are required to meet the rigorous data protection standards of the HITRUST CSF. Through collaboration with HITRUST, TEFCA upholds high data protection standards, acknowledging HITRUST as an effective solution for risk mitigation and compliance in healthcare.
Take the Next Step with A-LIGN
Whether you are on the path to becoming a QHIN within the TEFCA exchange or are just beginning your HITRUST compliance journey, A-LIGN can assist you with the certification process.
Working with A-LIGN offers you a high-quality and efficient audit experience, ensuring that your organization not only meets but exceeds the rigorous data protection standards required. With our expertise, your organization can confidently progress toward HITRUST Certification, paving the way for enhanced security, compliance, and trust in the rapidly evolving healthcare landscape.
For more information about achieving HITRUST Certification, contact us today.
Penetration testing is a critical component of a robust cybersecurity strategy, aiming to replicate real-world attack scenarios on the digital infrastructure. However, the effectiveness of penetration testing hinges on thorough preparation. In this blog, we’ll explore how you can prepare your organization for a penetration test, and how to turn readiness into an action that strengthens your digital defenses. Keep reading for a list of key activities and a penetration testing readiness checklist.
The purpose of preparation
The first step before you begin penetration testing is to complete pre-testing groundwork. But, this isn’t just about ticking boxes on a checklist, it is about a series of actions to improve your organization’s security posture. To start, organizations should:
- Align their security posture with industry best practices
- Identify risks that might be overlooked in daily operations
- Ensure personnel are aware, trained, and ready to respond
Penetration testing checklist
The detailed checklist outlined below is your map to a pen testing preparedness. It outlines the critical steps to gauge and elevate your readiness level for a penetration test, ultimately improving your defense and response strategies against cybersecurity threats.
Organizational preparation
Documented Objectives: The purpose of the penetration test should be clear and aligned with business objectives. These objectives will guide the scope and depth of your test.
Organizational Chart: A clear depiction of authority and responsibility helps in directing the flow of communication between stakeholders and the testing team.
Defined Responsibilities: Ensure that every role has clear guidelines on their involvement in the penetration testing process, including those who will lead the effort and those who will be audited.
Separation of Duties: Preventing conflicts of interest is paramount. Implementation should ensure that no single individual has control over all aspects of a task.
Board of Directors or Executive Oversight: High-level representation ensures that decisions are backed by the required budget and priority.
Policies and procedures
Hiring and Onboarding Procedures: Proper vetting and training of personnel helps to protect against insider threats.
Code of Conduct: This provides an ethical framework for employee actions and interactions with the penetration test.
Employee Handbook: All personnel should be acquainted with the rules and security measures specific to your organization.
Awareness and Ongoing Training Activities: Regular updates and training sessions keep security at the forefront of operation strategies.
Distribution of Policies: Policies are only effective when they are known. A clear communication plan is essential.
Personnel Evaluations: Regular assessments ensure that all staff members are continually adhering to security protocols.
Technical readiness
Inventory of Assets: Identifying and documenting all hardware and software assets enable thorough testing coverage.
Network and Application Architecture Details: This blueprint aids testers in navigating your systems effectively and efficiently.
Initial Vulnerability Scan: Conducting a preliminary scan gives you an overview of potential vulnerabilities and the breadth of issues that penetration testing might reveal.
Data Classification: Sensitivity classification enables testers to prioritize the most critical data, imitating real-world attack scenarios more accurately.
Controlling environmental variables
To mitigate surprises during a pen test, it’s essential to have control measures in place. These strategies secure the integrity of your systems and data, while also protecting the testing team from potential legal or professional ramifications.
Establishing test windows
Coordination with IT Operations: Keep them in the loop about the timing of the test to avoid conflicts in operations.
Notification to Third-Party Service Providers: Any systems controlled or managed by outside vendors should be scheduled for penetration testing in collaboration with them.
Legal and ethical considerations
Proper Authorization: Ensure that the testing team has explicit permission to probe your systems, applications, or network.
Impact Analysis: Conduct an assessment to determine the potential disruptions the test might cause and plan accordingly.
Scope Limitations: Clearly define what is in scope for testing to prevent unauthorized access to critical systems.
Client and Third-Party Notification: Notify your clients and third parties about the impending test, especially if there is potential for service disruptions.
Preparing your team for pen testing
A penetration test may challenge not just your cybersecurity measures, but also your human resources. Preparing your team involves psychological and professional readiness to handle the outcomes and implement necessary changes post-test.
Team skills assessment
Knowledge Base Evaluation: Determine whether your security team has the skills to decipher and act upon the findings of the penetration test.
Recruitment of Skills Gaps: For more complex and robust testing, consider hiring external specialists to complement your in-house team’s knowledge.
Psychological and social readiness
Contextualizing the Test as a Learning Opportunity: Frame the penetration test as a collaborative tool that can enhance the organization’s overall security posture.
Counseling for Potential Stress: High-stress environments, such as those experienced in cybersecurity exercises, can lead to burnout. Prepare your team mentally.
Responding to penetration test results
The end of a penetration testing engagement is not a wind-down to business as usual. Instead, it triggers a series of high-impact responses and analyses that feed back into your cybersecurity strategy, turning passive readiness into active protection.
Assessment of test results
Documentation of Findings: Every identified vulnerability must be exhaustively documented with information about its exploitability and potential impact.
Prioritization of Remediation Actions: Classify the findings based on their criticality and potential impact and create an action plan for remediation.
Implementation of remediation strategies
Immediate Fixes: Some vulnerabilities warrant an immediate fix to prevent exploitation. Implement these first.
Mid-Term Remediation Planning: Develop a more extensive plan to address issues in the medium term that require design changes or architectural improvements.
Long-Term Strategic Adaptation: Use the findings to inform long-term security strategy and architecture that are in line with current and future threats.
Penetration testing readiness is more than a requirement to tick off a compliance checklist. Committing to a comprehensive readiness strategy not only primes your organization for potential vulnerabilities, but also contributes to a culture of security-awareness at every level. When the time comes, your team can face the challenge with grit and knowledge.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has revolutionized many industries, but its rapid growth has also brought ethical, privacy, and security concerns. To address these challenges, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) devised a new standard, ISO/IEC 42001 (ISO 42001). Published on December 18, 2023, this standard provides guidance to organizations that design, develop, and deploy AI systems on factors such as transparency, accountability, bias identification and mitigation, safety, and privacy.
This article will explore the key elements of the standard, the benefits of implementing it, and next steps for organizations.
Structure of ISO 42001
Like several other ISO/IEC standards, ISO 42001 has several annexes that provide much of the detailed guidance organizations need. Here’s a quick breakdown of these annexes:
- Annex A: Management guide for AI system development, including a list of controls
- Annex B: Implementation guidance for the AI controls listed in Annex A, including data management processes
- Annex C: AI-related organizational objectives and risk sources
- Annex D: Domain- and sector-specific standards
Key themes of ISO 42001
ISO 42001 covers issues throughout the AI system lifecycle, from the initial concept phase to the final deployment and operation of the system. It is designed to help organizations manage the risks associated with AI and ensure that their AI systems are developed and used responsibly.
Some of the key requirements covered in the published standard include:
- Leadership: Top management should demonstrate leadership and commitment to the AI management system (AIMS) and establish policies and objectives that are consistent with the organization’s strategic direction.
- Planning: Identify and assess risks and opportunities associated with AI and develop a plan to address them.
- Support: Provide resources and support for the AIMS, including training, awareness, and communication.
- Operation: Establish processes and procedures for the development, deployment, and maintenance of AI systems.
- Performance evaluation: Monitor, measure, analyze, and evaluate the performance of AI systems and take corrective actions when necessary.
- Continual improvement: Continually improve the AIMS, and ensure that it remains relevant and effective.
Is ISO 42001 mandatory?
If your organization produces, develops, or uses AI, you may be wondering to what extent you should be scrambling to become certified in ISO 42001. In short, ISO 42001 is a voluntary standard and is not legally binding. However, given its significance and emerging recognition, it is highly likely to become the benchmark for AI management systems in the future. Organizations should anticipate possible regulatory developments and consider proactively adopting ISO 42001.
Organizational roles and responsibilities
Effectively implementing ISO 42001 starts with identifying members of your organization in key roles related to AI:
- AI provider: An organization or entity that provides products or services that uses one or more AI systems. AI providers encompass AI platform providers and AI product or service providers.
- AI producer: An organization or entity that designs, develops, tests and deploys products or services that use one or more AI system. This includes AI developers that are concerned with the development of AI services and products. Examples of AI developers include model designers, implementers, computation verifiers, and model verifiers.
- AI customer: An organization or entity that uses an AI product or service either directly or by its provision to AI users.
Benefits of implementing ISO 42001
Though few organizations relish the idea of more audits, there are good reasons to move forward with certification sooner rather than later. (Plus, if you practice strategic compliance and consolidate your audits, adding ISO 42001 to your compliance program may be easier than you think.)
Managing AI risks and opportunities
ISO 42001 provides organizations with a systematic approach to identify, evaluate, and address the risks associated with AI. This can help organizations mitigate the risks of AI and protect themselves from potential harm.
Competitive advantage
Implementing ISO 42001 enables organizations to showcase their early adopter status, demonstrating their commitment to responsible AI use. This can enhance stakeholders’ trust and distinguish the organization from competitors.
Cost savings and improved efficiency
By incorporating ISO 42001’s best practices, organizations can streamline their AI processes, identify and rectify vulnerabilities earlier, and reduce the potential financial and reputational costs associated with AI failures.
ISO 42001: Next steps for businesses
To navigate the complex landscape of AI governance and compliance, compliance managers should consider the following steps:
- Purchase and understand the standard: Obtain a copy of ISO/IEC 42001 and familiarize yourself with its provisions. It is crucial to understand the requirements, recommendations, and other applicable requirements (i.e. ISO/IEC 22989, ISO/IEC 23894) to effectively implement the standard.
- Start internal talks about certification: Initiating conversations about the certification audit process within your organization is essential. Understanding the steps involved and allocating necessary resources will ensure a smooth transition toward ISO 42001 compliance.
- Get a readiness assessment: Consider engaging a trusted compliance partner like A-LIGN to conduct a readiness assessment tailored to your organization’s specific needs. This assessment will help identify any gaps and provide guidance on achieving ISO 42001 compliance.
As the AI landscape continues to evolve, embracing ISO 42001 will position businesses as leaders in the field, fostering trust and ensuring the long-term success of AI initiatives. Stay ahead in the AI era by leveraging ISO 42001 and building a solid foundation for your AI management system.
Securing cloud infrastructure is a top priority for modern organizations. A commonly recognized compliance standard for cloud service providers (CSPs) is the Cloud Computing Compliance Criteria Catalogue or C5. C5 was first introduced by the Federal Office for Information Security (BSI) in Germany in 2016. In this blog post, we will provide a comprehensive guide to C5 attestation, highlighting its fundamental principles and what organizations need to do to achieve compliance.
Why is C5 attestation important for CSPs?
C5 attestation provides a comprehensive framework of standard security controls for CSPs providing cloud services. The security controls are tailored to meet the needs of CSPs and provide a foundation for secure cloud services. By complying with the C5 requirements, CSPs can demonstrate a high level of security maturity and gain a competitive advantage in the market.
What are the C5 requirements?
The C5 criteria are divided into 17 categories and objectives initially based on ISO 27001:2013 Annex A. These categories include Asset Management, Physical Security, Identity and Access Management, and countless others. The C5 criteria also considers a wide range of standards and publications, including the AICPA Trust Services Criteria, ISO 27001, ISO 27002, ISO 27017, the Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) Cloud Control Matrix (CCM), and the German IT baseline protection manual (BSI-IT-Grundschutz). CSPs that are already compliant with one or more of these publications should consider their preparedness and applicability to the C5 criteria.
What is the C5 examination process?
The Federal Office for Information Security has dictated that C5 assessments should be performed using nationally and internationally established standards, namely ISAE 3000 in conjunction with the AICPA’s AT-C section 105 “Concepts Common to All Attestation Engagements” and AT-C section 205 “Examination Engagements.” The catalog dictates that conformity with the C5 criteria should always be provided using the ISAE 3000 audit standard.
A good starting place for organizations new to C5 is a SOC 2 plus C5 readiness assessment. Your assessor can help you understand the requirements, assess your current status, and identify potential gaps. After the readiness assessment is completed, your team will have a roadmap to follow that can make the final examination easier for all parties involved.
Whether a readiness assessment is needed or not, full compliance should be achieved via a SOC 2 plus C5 attestation with the ISAE 3000 integration. The engagement can be completed as a Type 1, attesting to the design of the C5 control set, or a Type 2, testing the design, implementation, and operating effectiveness of the organization’s controls as they meet the SOC 2 and C5 criteria.
Staying up to date with C5 requirements
The BSI updates the C5 controls regularly to reflect the changing cybersecurity landscape. Organizations can stay updated on new or modified controls by regularly checking the BSI website. Failure to comply with the updated controls could result in non-compliances, fines, and reputational damage.
Updates to the C5 Attestation
Germany has tightened its rules about processing health data as more companies rely on cloud computing to safely transmit and access patient information.
The new Section 393 SGB V provides “minimum technical standards” for IT systems and cloud computing and will require many companies to get a new C5 certificate.
According to the new requirements, health and social data can only be processed in Germany, in an EU or EEA member state, or in a third country adequacy decision by the European Commission. The data processing entity should also have a business establishment in Germany.
Section 393 SGB V also requires stricter technical and security compliance requirements. Companies that process data using cloud computing services need the following:
- Appropriate technical and organizational measures for data security.
- A current C5 certificate. Until June 30, 2025, a Type 1 certificate is considered current. Beginning in July 2025, a new Type 2 certificate is required.
- To implement C5 certificate conditions and criteria.
Health care providers and insurance companies will have additional technical and organizational requirements based on the type of provider or institution.
Medical research and projects may be subject to these new requirements too, though the scope isn’t immediately clear. Companies that conduct clinical trials with pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and diagnostics are less likely to be impacted by these new standards than trials that collect real-world data, like non-interventional studies.
Getting started with C5
Achieving C5 attestation is essential for security-conscious CSPs that want to demonstrate their commitment to security to clients and customers. The process requires dedication, effort, and a thorough understanding of the C5 catalogue, but the benefits are undeniable. By embracing C5, organizations can establish a foundation for secure cloud services, improve their security posture, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
Contact A-LIGN to learn more about C5 attestation.
When it comes to pursuing ISO/IEC 27001 (ISO 27001) and/or ISO/IEC 27701 (ISO 27701) certifications, credibility of your audit firm and quality of your final report and certificate are paramount to showing your dedication to security. With many organizations expanding their businesses into international markets, they must navigate compliance laws and regulations around the world.
A-LIGN recognizes the complex compliance needs for businesses that require cybersecurity compliance assessments in the U.S. and EMEA region. To cater to this growing demand, A-LIGN has successfully pursued and obtained accreditation from both ANAB and UKAS specifically to the ISO 27001 and ISO 27701 standards.
With multiple regional regulations to adhere to and multiple certification bodies to choose from, organizations may be wondering which certification route to choose. In this blog, we break down the differences between accreditation bodies such as ANAB and UKAS, and how your business can leverage the power of both accreditations for ISO 27001 and/or ISO 27701 certifications.
The importance of ISO/IEC 27001 & ISO/IEC 27701 around the globe
Established by the International Organization of Standards (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), ISO 27001 and ISO 27701 are internationally recognized cybersecurity frameworks.
The standards of ISO 27001 focus on establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continuously improving an organization’s Information Security Management Systems (ISMS).
On the other hand, the ISO/IEC 27701 standard assists organizations in protecting and controlling personally identifiable information (PII), implementing a Privacy Information Management System (PIMS), enhancing data protection measures, and ensuring compliance with global privacy regulations.
By showcasing compliance with ISO 27001 and ISO 27701, businesses not only instill confidence in their stakeholders, but also gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
The distinction between accreditation bodies – ANAB vs. UKAS
Accreditation bodies play a crucial role in upholding the integrity and credibility of compliance assessments. As many organizations expand their business into different regions of the world, they may be required to pursue ISO 27001 and/or ISO 27701 certifications with different accreditation bodies.
What is ANAB?
Within the US, there are only three International Accreditation Forum (IAF) recognized accreditation bodies that can certify both ISO 27001 & 27701. Given A-LIGN’s passion for quality, we have committed to being accredited to ANAB.
The ANSI National Accreditation Board (ANAB) is a multi-disciplinary accreditation body, serving more than 2,500 organizations in 80 countries. ANAB provides accreditation and training services and builds assessment structures for programs across many industries.
Established in 1989 as Registrar Accreditation Board (RAB) and considered the most reputable accreditation body in the United States, ANAB strives for a high level of quality when it comes to ISO 27001 and ISO 27701 certification standards. Pursuing ISO certifications with ANAB may be the best fit for organizations seeking exceptional compliance frameworks in the United States.
What is UKAS?
Within the United Kingdom, there is only one IAF recognized accreditation body that can certify both ISO 27001 & 27701.
The United Kingdom Accreditation Service (UKAS) was established in 1995 and is considered the most reputable accreditation body in the EMEA region. UKAS is a government-appointed body that assesses and accredits organizations that provide certification, testing, inspection, and calibration services.
For EMEA-based compliance assessment services, UKAS is a preferred accreditation body to ensure the highest standards of competence and integrity. UKAS brings an unparalleled level of credibility and accuracy of ISO 27001 and ISO 27701 certifications in the EMEA region, instilling confidence in organizations displaying their dedication to security.
Investing in quality for ISO/IEC 27001 & ISO/IEC 27701 compliance success
While organizations have many factors to consider when selecting an auditor for ISO 27001 and/or ISO 27701 certifications, it is imperative for businesses to consider the quality and reputation of the assessor and the accreditation body.
To learn more about choosing the best organization for your ISMS and PIMS certification needs, visit our blog, Examining the Different Certification Bodies for Certification.
With mounting security concerns in this digital age, businesses are required to adhere to even stricter standards to ensure the safeguarding of their sensitive data. Choosing the right assessor can be a critical decision for businesses looking to build a strong compliance program.
To avoid a low-quality, check-the-box audit experience, businesses should only consider working with a third-party assessment organization accredited by a reputable body.
ISO/IEC 27001 & ISO/IEC 27701 with A-LIGN
As an accredited certification body, A-LIGN has worked with 900 customers to complete more than 2,000 ISO audits, earning a customer satisfaction rating of 94%. It is our goal to provide a high-quality and efficient audit experience for every organization, no matter their location in the world.
For this reason, we are proud to be accredited by ANAB and UKAS to provide ISO 27001 and ISO 27701 services for organizations adhering to cybersecurity compliance regulations in the United States, EMEA regions, or both. These accreditation bodies strive to meet the highest standards of quality and impartiality, so opting for ANAB and/or UKAS-accredited audits means embracing a comprehensive and trustworthy compliance journey.
At A-LIGN, we pride ourselves in being a leading cybersecurity compliance partner for over 4,000 organizations across the globe. We provide a world-class audit experience unparalleled in quality and efficiency for a wide variety of security assessments. To learn more about starting your ISO 27001 and/or ISO 27701 compliance journey, contact us today.
Healthcare organizations handling electronic protected health information (ePHI) must stay vigilant and protect their data from cyber-attacks. Complying with HIPAA standards is essential for these businesses to show they have the correct controls in place to safeguard sensitive information.
Getting started with your HIPAA compliance journey can be confusing, but we have created a HIPAA readiness checklist to set your business up for success as you pursue your upcoming HIPAA assessment.
Download the HIPAA checklist PDF!
The importance of HIPAA compliance
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) is a federal law requiring organizations to uphold stringent privacy safeguards for individually identifiable health information, ensuring security of patient data.
Organizations managing ePHI are expected to undergo a HIPAA compliance assessment to validate the business has controls in place to safeguard data.
By complying with HIPAA standards, companies not only meet legal obligations, but also avoid severe financial penalties due to non-compliance. Most importantly, HIPAA compliance instills peace of mind and showcases the business’s commitment to cybersecurity to their valued clients and other stakeholders.
Understanding the HIPAA readiness checklist
Once your team is prepared and has knowledge of HIPAA compliance and the assessment process, you can kick off your compliance journey with our HIPAA readiness checklist.
By adhering to these comprehensive steps, your organization not only showcases its commitment to compliance, but also fosters a culture of security that lasts far beyond the audit.
Security rule – administrative safeguard
Security management process
Establish and audit key policies and procedures to prevent, detect, contain, and correct security violations, such as:
- HIPAA Policies and Procedures
- Information Security Policies and procedures (should include key assignments for security responsibilities)
- Access and Authorization Policies and Procedures (if not included in Information Security Policies)
- Workforce Clearance Policies and Procedures
- Physical Security Policies and Procedures
- Incident Management and Incident Response Policies and Procedures
- Network Diagrams
- Risk Management Process Policies and Procedures
- Completed Risk Assessment
- Vulnerability Assessment
- Sanctions
Assign security responsibility
Identify the security official who is responsible for the development and implementation of the policies and procedures required under HIPAA. This individual will be responsible for the development, implementation, and enforcement of HIPAA Security Rule policies and procedures. The HIPAA Privacy Officer can also hold these responsibilities.
Workforce security and information and access management
Define policies and procedures to ensure that all members of the workforce have appropriate access to ePHI, as provided under the Information Access Management standard and to prevent those who do not have appropriate access from obtaining access to ePHI. Management should also formally define policies and procedures surrounding workforce management with access to PHI/ePHI to include:
- Authorization and/or Supervision procedures
- Access Modifications
- Hiring and Workforce Clearance Procedure (including background checks)
- Termination Procedures
- Isolating Health Care Clearinghouse functions
Security awareness and training
Establish a security awareness and training program for all members of the workforce, including management. Management should then implement a Security Awareness and Training program that is completed at least annually and includes:
- Frequent Security Reminders
- Protection Malicious Software
- Log-in Monitoring and Password Management
Security incident procedures
Management should create policies and procedures to address security incidents as well as Incident Management policies and procedures that include the following:
- Incident identification & classification
- Incident response
- Incident tracking
- Root cause and system impact analysis
- Escalation
- Changes implemented for remediating incidents
- Critical security incident response
- Incident reporting
Contingency plan
Management should establish and implement policies and procedures for responding to an emergency or other occurrence that damages systems that contain ePHI. Management should also establish Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery (BCDR) policies and procedures that include:
- BCDR Plan
- BCDR Testing, on at least an annual basis
- Backup configurations (incremental and full backups)
- Offsite backup rotation and/or replication
- Backup restoration
Evaluations
Management should perform a periodic technical and nontechnical evaluation based initially upon the standards implemented under the HIPAA Security Rule. Evaluations of controls should be documented to mitigate identified risks, vulnerabilities, deviations, and control gaps identified as part of the various evaluations (e.g. risk assessments, vulnerability scans). Note that having a HIPAA security rule risk assessment is a stringent requirement within the HIPAA law. Organizations could have legal or compliance ramifications if they have not performed a risk assessment of their ePHI data.
These controls should be documented in an Internal Controls Matrix (ICM) that includes the following attributes for each control:
- Control owner
- Control frequency
- Control type (i.e., preventative, detective or corrective)
- Control execution (i.e., automatic vs. manual)
Security rule – physical safeguard
Facility access controls
Management should implement policies and procedures to limit physical access to its electronic information systems and the facility or facilities in which they are housed, while ensuring that properly authorized access is allowed. Management should establish Physical Access policies and procedures that include:
- Facility access
- Visitor access and badge inventory
- Surveillance retention periods
- Emergency procedures
- Facility Maintenance
- Access to areas containing PHI
Workstation security and use
The organization should determine whether they are a covered entity. Management should implement physical safeguards for all workstations that access ePHI to restrict access to authorized users. Management should also define policies and procedures regarding the safeguarding and use of workstations (workstations on wheels) to include:
- Physical Access to workstations limited to authorize personnel
- Prohibiting non-business activity on workstations
Device and media controls
Management should implement policies and procedures that govern the receipt and removal of hardware and electronic media that contain ePHI into, out of, and within the facility. Management should also formally define policies and procedures regarding hardware and removable media that include:
- Hardware and media accountability
- Acceptable Use
- Maintenance records for the movement of hardware and media
- Data disposal and destruction
- Asset Inventory
- Removable Media
- Bring your own device (BYOD)
Security rule – technical safeguards
Access controls
Management should implement technical policies and procedures for electronic information systems that maintain ePHI to allow access only to those persons or software programs that are required. Management should also formally define and follow key information security controls that include:
- Access provisioning and removal
- Role-based access privileges
- Standardized authentication procedures for all systems
- Standardized, minimum password requirements for all user and system accounts
- External access procedures
- Emergency access procedures
Audit controls
Management should implement hardware, software, and/or procedural mechanisms that record and examine activity in information systems that contain or use ePHI. Management should also formally document policies and procedures regarding information systems activity review and internal audit functions and include:
- Documented review process
- Audit logging
- Physical access logs
- Policy and Procedure Review
- Periodic internal controls reviews
Integrity controls and transmission security
Management should outline and implement security measures to ensure that electronically transmitted ePHI is not improperly modified without detection until disposed of. Management should also implement standardized encryption mechanisms that provide encryption at rest and encryption in transit.
File Integrity Monitoring (FIM) should also be utilized to ensure only authorized changes are deployed into production environments.
Person or entity authentication
Management should develop policies and procedures to verify that a person or entity seeking access to ePHI is the one claimed, as well as formally document policies and procedures around information security that include:
- Authentication into Networks, Databases, Applications and VPN in the production environments
- Administrative access
- Password Configurations
- Audit Logs
Security rule – organizational requirements
Business associate contracts and documentation
Management should maintain business associate agreements (BAA) with businesses that create, receive maintain, or transmit ePHI. Management should also maintain documentation of HIPAA policies and procedures as required for 6 years and maintain business associate agreements in compliance with the HIPAA Security Rule.
- Business Associates who utilize subcontractors in the processing, transmission, or storage of ePHI must maintain a BAA.
- Business associates are required to adhere to security, incident response, and breach notification procedures outlined by the covered entity entered into an agreement with.
- Documentation should be maintained for a minimum of 6 years per HIPAA Security Rule guidelines.
Breach notification
If the organization creates, receives, maintains, or transmits PHI/ ePHI, management should document Breach Notification policies and procedures. Breach Notification policies and procedures address the following:
- Breach Risk Assessment
- Was ePHI encrypted?
- What data was exposed?
- Who accessed the PHI/ePHI?
- What is the likelihood of further use of exposed data?
- What controls are in place to mitigate impact?
- Breach Notification Letters or Emails
Privacy rule and individual rights
If your organization is a covered entity or if your organization creates, processes, transmits, or stores PHI, if applicable, management should designate a HIPAA Privacy Officer who is responsible for the development, implementation, and enforcement of HIPAA compliant policies and procedures.
Management should formally document HIPAA Privacy policies and procedures, Privacy Notices and/or a Statement of Privacy Practices that address the following:
- Obtaining authorizations
- Address individual rights to consent or opt-out.
- Methods of collection
- Use, disclosure, retention for a minimum of six years, and disposal of PHI
- Disclosure of PHI to third parties and the purpose of use
- Security for privacy
- Monitoring and enforcement of sanctions for inappropriate use and disclosure of PHI
Partner with A-LIGN for your HIPAA compliance journey
Achieving and maintaining HIPAA compliance is paramount for organizations handling ePHI. Not only is it essential to assure stakeholders their sensitive data is safe in your hands, but it is also critical to stay compliant to avoid cyber-attacks and financial penalties.
By working with an experienced 3PAO like A-LIGN, your business can expect a world-class audit experience unparalleled in quality and efficiency. Stay ahead of the curve and get audit ready by taking advantage of our comprehensive HIPAA readiness checklist. Download our readiness checklist now!
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity and compliance, staying ahead of the curve has become imperative for businesses worldwide. As technology advances, so do the methods employed by bad actors seeking to exploit vulnerabilities. Recent surveys and reports reveal several notable cybersecurity and compliance trends that businesses should pay attention to.
In this blog, we delve into key trends and strategies that define the current state of cybersecurity and compliance, shedding light on the importance of continuous monitoring, the role of artificial intelligence, and the need for a comprehensive audit strategy.
AI and machine learning gain traction
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing how organizations approach cybersecurity and compliance. The U.S. Census Bureau anticipates that the use of AI by businesses to directly produce goods and services will dramatically increase in the first half of 2024, particularly for the information sector and the professional, technical, and scientific services sector. Another recent survey found that 78% of C-suite leaders reported their companies using AI in some capacity.
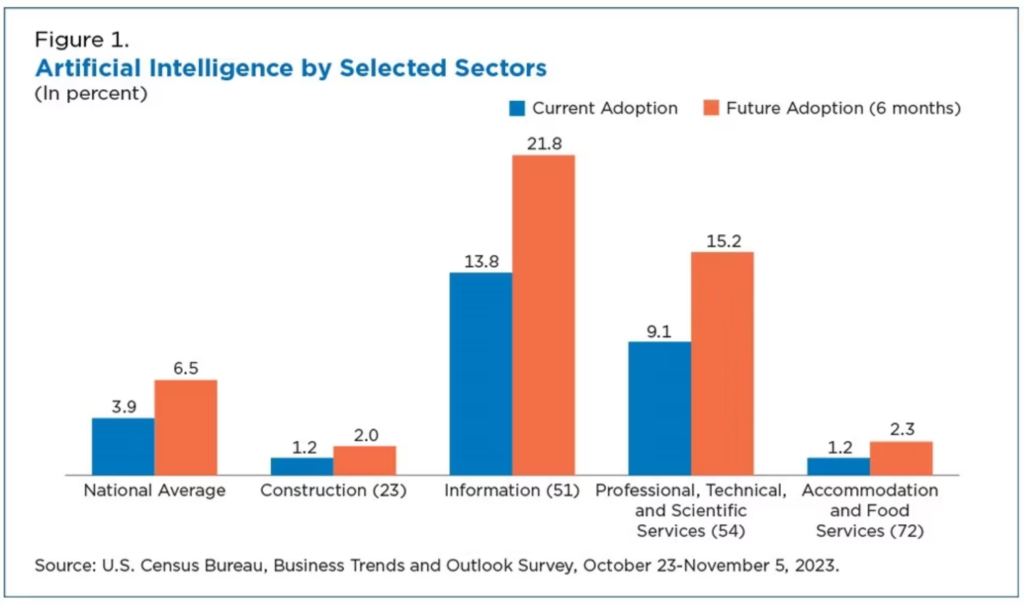
The increasing use of AI and machine learning (ML) tools enables companies to swiftly analyze vast amounts of data, identifying security risks more efficiently than ever. For example, a team that leverages AI in their security information and event management (SIEM) will build efficiency as AI filters out false positives, enabling the Security Analysts to focus and remediate real threats. Also, AI integrated in firewalls and malware solutions can help automate some controls and save the organization time and money.
The efficiency created by AI tools can make it more practical for businesses to monitor risk proactively, rather than waiting for a major security incident to arise and kick staff into gear. Staying ahead of the curve makes compliance with major security and privacy standards less of a headache because controls are already integrated into regular business operations.
However, using AI and ML for compliance is a double-edged sword that requires vigilance, as malicious actors are also harnessing AI to accelerate hacking attempts. As regulatory bodies adapt — illustrated by the progression of ISO 42001 — organizations must proactively embrace AI while remaining cognizant of the associated risks.
Continuous monitoring wins over point-in-time audits
In the past, compliance was seen as an annual checkpoint activity — something businesses had to do once per year to check a box. But with the threat landscape evolving so rapidly, performing compliance assessments at a single point in time is no longer enough. To safeguard vital company information and avoid catastrophic financial losses, catching potential threats early on is key. According to an IBM report, the global average cost of a data breach in 2023 was $4.45 million, a 15% increase over three years.
Leading organizations are embracing continuous monitoring to regularly validate security controls and compliance with standards. Incorporating regular vulnerability scans and automated attack surface scans ensures that security best practices are implemented across the business throughout the year. This approach is more than a mere checkbox for compliance; it is a commitment to safeguarding sensitive data.
To get a real-time look at compliance within an organization, many cybersecurity teams are turning to software. Depending on the software, organizations can view their current status and potential vulnerabilities, conduct automated scans, track data security metrics, monitor changes in their systems, and more. With the right tools in place, it is easier for teams to see a big picture view of the security landscape and proactively identify threats.
No business is safe from cyber crime
The year 2023 witnessed high-profile cyberattacks that underscored the vulnerability of organizations, regardless of size or industry. Here are a few notable examples:
- MGM Resorts International experienced a cyberattack in September 2023 that it expected would cost the company $100 million. Hackers breached MGM’s systems to steal data for extortion, and the company was forced to shut down some of its systems at its casino resorts across the nation.
- In May, a ransomware group infiltrated Progress Software’s managed file transfer (MFT) solution known as MOVEit Transfer, stealing sensitive data from hundreds of organizations.
Despite these high-profile stories involving massive corporations, 43% of cyberattacks target small businesses, and the average employee of a small business with less than 100 employees will receive 350% more social engineering attacks than an employee of a larger enterprise.
Cybercriminals frequently target startups and smaller organizations specifically because of their lack of security resources. Even businesses with substantial security teams and resources are not immune, raising a crucial question for smaller entities: Can your business withstand a cyberattack?
When it comes to compliance, quality matters
In the Compliance Benchmark Report of 2023, 28% of respondents identified the quality of the final report as the most important factor when selecting cybersecurity and compliance auditors. This underscores the value of audit reports for maintaining compliance and satisfying business partners and to enhance overall IT processes.
Quality is equally crucial for other cybersecurity services such as penetration testing. As the stats we’ve covered illustrate, the difference between a comprehensive cybersecurity program and an inadequate one can add up to millions of dollars in remediation measures and lost revenue. Although the cost of services may be a factor, the focus should be on finding an experienced team that conducts thorough assessments of security controls to help organizations identify vulnerabilities before hackers do. Businesses that value cybersecurity are already making quality a priority.
Audit consolidation improves efficiency and reduces risk
Navigating the audit landscape requires a thoughtful and strategic approach. Spreading out compliance audits throughout the year aligns with the concept of continuous monitoring and helps organizations evaluate threats and vulnerabilities on a regular basis. But because of the ongoing resource requirements involved with cybersecurity and compliance, it’s no surprise that organizations are looking for ways to make the process more efficient. Instead of hiring multiple auditors in an ad hoc fashion, businesses are more frequently opting for audit consolidation with a single, trusted partner.
Constant audits may not sound enjoyable, but if organizations make cybersecurity a priority year-round, compliance will be easy, efficient, and cost-effective. The right compliance partner can help businesses streamline compliance so that a singular audit process will result in multiple assessment reports. That means audits are less of a headache and the business minimizes cyber-related risks — a win-win.
The importance of proactive cybersecurity in 2024 and beyond
The current state of cybersecurity and compliance demands a proactive and adaptive approach. As technology evolves, so do the threats, making continuous monitoring, AI integration, and quality assurance crucial components of a comprehensive strategy. Acknowledging that no business is immune to cyber threats is the first step toward building a resilient defense. By embracing a culture of security, prioritizing quality in audits and cybersecurity measures, and adopting a consolidated and strategic approach to compliance, organizations can navigate the complex landscape and safeguard their digital assets in an era where cybersecurity is more critical than ever.


We are pleased to announce the appointment of Jennifer Hawks as the new Federal Practice Lead. Jennifer has been a guiding force in U.S. Government cybersecurity governance, risk, and compliance for over two decades.
Prior to joining A-LIGN, Jennifer held the role of VP of Government Services at NCC Group and provided assessment and advisory services for various cybersecurity frameworks, including FedRAMP, StateRAMP, TXRAMP, CMMC/NIST 800-171, NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF), and FISMA/NIST RMF. Earlier in her career, Jennifer led a cybersecurity startup to become a FedRAMP third-party assessment organization (3PAO) and assessed security risks in the federal government’s vendor and supplier ecosystem within the US Department of Defense (DoD) supply chain at Booz Allen Hamilton.
In addition to the appointment of Jennifer, we are excited to introduce LaTara Allen as the Associate Director of Federal Services. LaTara has over 20 years of experience navigating the complexities of federal programs while optimizing the processes and service delivery of FedRAMP, StateRAMP, and CMMC/NIST 800-171 assessments.
“As a top 3 FedRAMP 3PAO and serving more than 150 clients, A-LIGN is committed to providing best-in-class compliance and cybersecurity solutions for our clients,” stated Steve Simmons, COO. “With Jennifer Hawks leading our federal practice and working alongside LaTara Allen, our strengthened staff will enable us to guide our clients through complex federal compliance requirements, providing them with the assurance and guidance they need to achieve their goals.”
Latest Additions Solidify Leadership in Delivering High-Quality and Efficient Federal Assessments
As a leading assessor for the US Government, A-LIGN is pleased to offer an end-to-end compliance solution that simplifies the complex reporting process to deliver high-quality reports and certifications government agencies require from their cloud service providers. With an extensive network of resources, experience, and professional relationships, we are dedicated to ensuring organizations are prepared and authorized to support government agencies by minimizing risks and safeguarding data.
These additions are a commitment from A-LIGN to provide a world-class audit experience with senior talent to allow our clients to continue to win federal contracts and grow their business.
To learn more about A-LIGN’s trusted federal services including FedRAMP, StateRAMP, CMMC, FISMA, and more, visit https://www.a-lign.com/government.